CT Scan Basics
Understand the Foundations of Computed Tomography
CT (Computed Tomography) एक advanced medical imaging technique है जो body के internal structures की cross-sectional images बनाती है। CT scan traditional X-ray से अलग है क्योंकि यह body को कई angles से scan करता है और detailed 3D slices प्रदान करता है।
यह diagnostic radiography में revolution लेकर आया है और diseases की early detection तथा treatment planning में बहुत उपयोगी है।
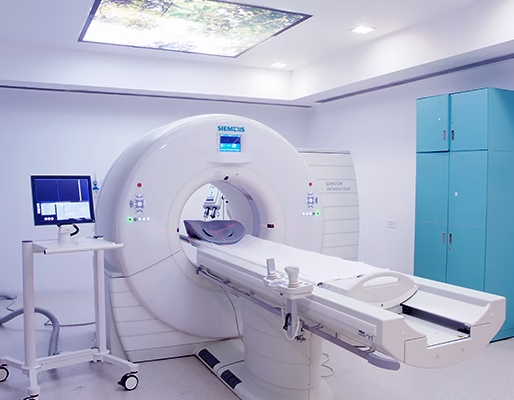
How Does a CT Scanner Work?
CT scan system कुछ key components से मिलकर बना होता है:
🔸 Gantry: Doughnut-shaped part जिसमें X-ray tube और detectors rotate करते हैं
🔸 X-ray Tube: High-energy X-rays emit करता है जो patient के body से गुजरते हैं
🔸 Detector Array: Patient के opposite side पर लगे होते हैं — यह X-rays को capture करते हैं
🔸 Computer System: Data को reconstruct करके 2D या 3D images बनाता है
CT Imaging Process – Step-by-Step
Patient Positioning: Patient table पर लेटा होता है और Gantry के बीच slide किया जाता है
X-ray Emission: X-ray tube body के चारों तरफ घूमता है
Image Capture: Detectors transmitted rays को collect करते हैं
Reconstruction: Computer captured data को detailed slice images में convert करता है
Image Adjustment – Window Width and Level
Window Width (WW):
Controls contrast of the image
➤ Narrow WW = High contrast
➤ Wide WW = Low contrast
Window Level (WL):
Controls brightness
➤ Low WL = Brighter image
➤ High WL = Darker image
These adjustments help radiographers visualize specific tissues (e.g., lung, soft tissue, bone) more effectively.
Use of Contrast Media in CT
Use if Contrast Media in CT
Contrast Type | Used For |
|---|---|
Iodine-based | Blood vessels, tumors |
Oral contrast | GI tract visualization |
Rectal contrast | Colon/rectum exams |
Contrast media organs और vascular structures को highlight करता है, जिससे pathology detection आसान होता है।
Advantages of CT Scanning
High-resolution cross-sectional imaging
Fast acquisition (ideal for trauma and stroke)
Visualization of bone, soft tissue, and blood vessels simultaneously
Ideal for 3D reconstruction and pre-surgical planning
